Making History by
Leaving Little Behind
A Powerful Story of Diesel Innovation
Diesel Engine Technology - See the Evolution
Overview
To meet increasingly stringent emissions regulations, John Deere has followed a carefully planned building-block approach. We have systematically adopted new technologies and integrated them with our field-proven solutions to meet each regulatory tier.
The building blocks of our Integrated Emissions Control system
Expand AllCollapse All
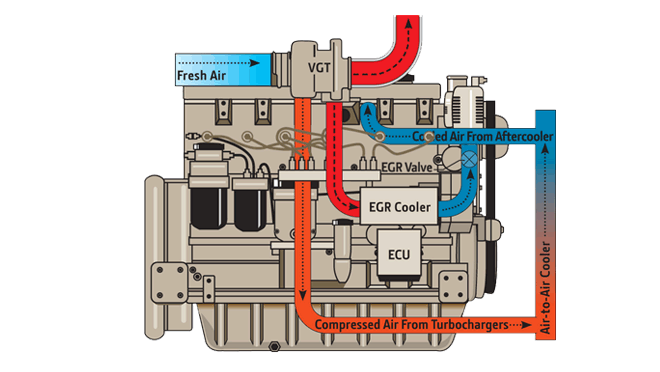
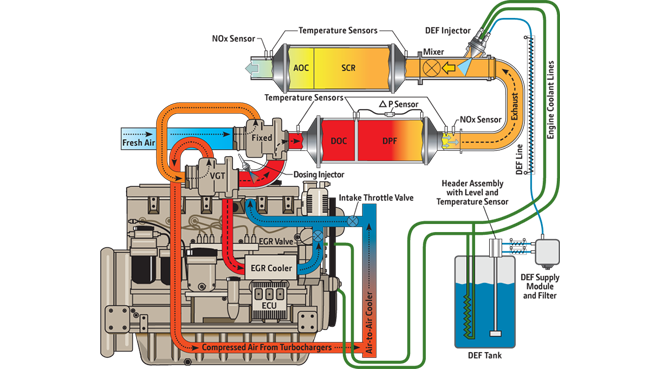
John Deere was the first engine manufacturer to widely commercialise cooled exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) and variable geometry turbocharger (VGT) technologies in off-highway applications, introducing them in 2005 with the start of Tier 3/Stage III A regulations. At appropriate levels of engine operation, the EGR valve opens and measured amounts of cooled exhaust gas are routed back into the intake manifold and mixed with the incoming fresh air. Since this process removes oxygen from the air, the exhaust temperatures in the combustion process are lowered and the levels of nitrogen oxides (NOx) are reduced.
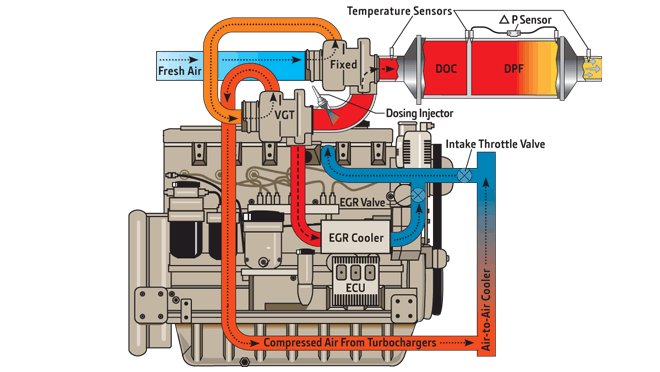
To achieve Interim Tier 4/Stage III B emissions requirements, we added a catalysed exhaust filter that contains a diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC) and a diesel particulate filter (DPF). The DOC reacts with exhaust gases to reduce carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, and some particulate matter (PM). The downstream DPF forces exhaust gases to flow through porous channel walls, trapping and holding the remaining PM. During normal operating conditions (temperature, load, and speed) the engine's natural heat breaks down the PM and cleans the exhaust filter. An exhaust filter also has the benefit of replacing the muffler in most applications.
Selective catalytic reduction (SCR) combined with our proven Interim Tier 4/Stage III B engine platform is the best solution to achieve Final Tier 4/Stage IV emissions compliance. This technology utilises a urea-based additive, sometimes referred to as diesel exhaust fluid (DEF). The ammonia in the urea mixes with engine exhaust gases in the SCR catalyst to reduce NOx — converting it to nitrogen and water vapour. This vapour is then expelled through the exhaust pipe. Why did John Deere wait to deploy SCR? We didn't need it before now. Our advanced cooled EGR system met all previous NOx requirements without the need for SCR and a second fluid. We are adding SCR at a time when the infrastructure for DEF is more established and its use is more accepted by equipment owners. SCR has been successfully used in on-highway applications, and the components are now more developed for off-highway applications.
The benefits of choosing John Deere engines
Expand AllCollapse All
The John Deere Integrated Emissions Control system for Final Tier 4/Stage IV compliance is optimised to meet emissions regulations while delivering improved performance and world-class fluid economy.
John Deere established an unparalleled record of fuel economy with our best-in-class Tier 3/Stage III A engines. Our Interim Tier 4/Stage III B and Final Tier 4/Stage IV technology solutions continue that efficiency by maximising total fluid economy. With fuel economy gains achieved through increased injection pressures and lower DEF dosing rates delivered by the optimised SCR system, John Deere Final Tier 4/Stage IV engines will meet or improve upon the current total fluid economy of our Interim Tier 4/Stage III B engine models. John Deere Final Tier 4/Stage IV engines operate efficiently with ultra-low sulfur diesel as well as B5 to B20 blends, providing optimal performance and fuel-choice flexibility.
John Deere has a strong advantage when it comes to off-highway expertise. Our Final Tier 4/Stage IV engines offer a field-proven, fluid-efficient approach that stands up to the tough demands of off-highway environments.
John Deere is one of the few manufacturers that designs engines as well as construction, forestry, and agricultural equipment — which gives us a unique advantage in designing and integrating the engine, drivetrain, hydraulics, electronic control unit (ECU), cooling package, and other vehicle systems for optimised efficiency. This integrated process maximises performance, operator convenience, fuel economy and overall value for John Deere machine owners as well as John Deere OEM customers.
The proven John Deere worldwide dealer network of over 4,000 service locations is prepared to fully support customers and their Final Tier 4/Stage IV engines. John Deere dealers are highly trained to help customers with the performance, service, and support of these new engines and to optimise total machine efficiency.
Reducing emissions while maximizing performance
John Deere engines provide the ultimate combination of performance, fuel economy, and emissions compliance. To meet evolving emissions regulations, John Deere worked closely with equipment manufacturers to identify engine technologies that best suited their needs, while also reducing carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter.
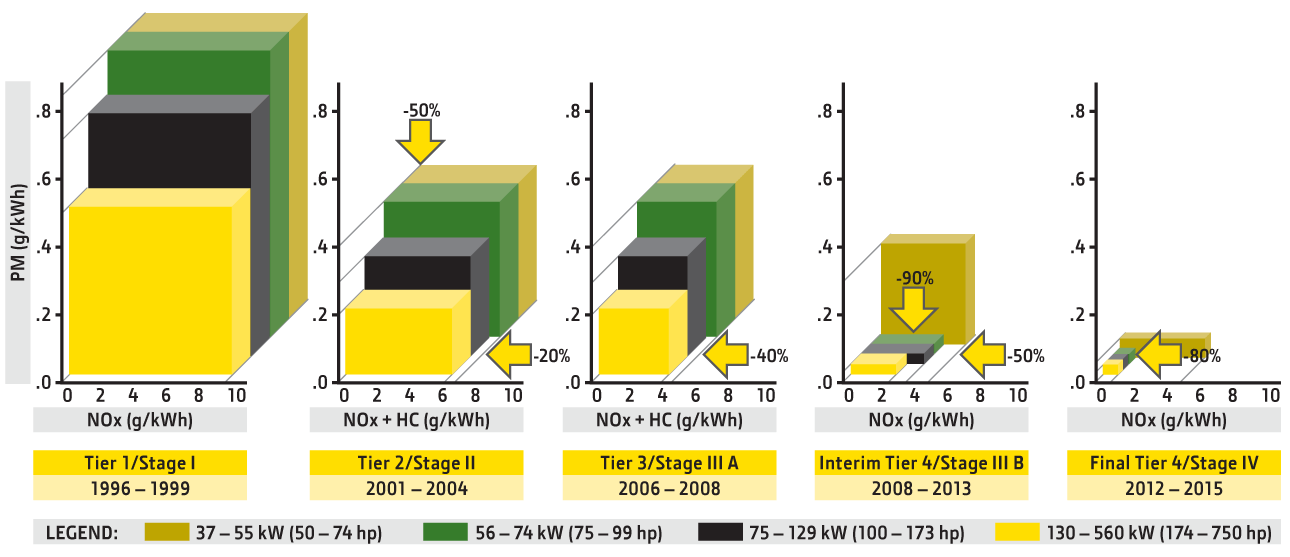
The first regulations for new nonroad diesel engines over 37 kW (50 hp) began in 1996 when John Deere launched PowerTech™, a new breed of engines that met Tier 1/Stage I emissions regulations. Since then, several tiers and stages have been developed to meet tightened regulations, with the Final Tier 4/Stage IV to be implemented by 2015.
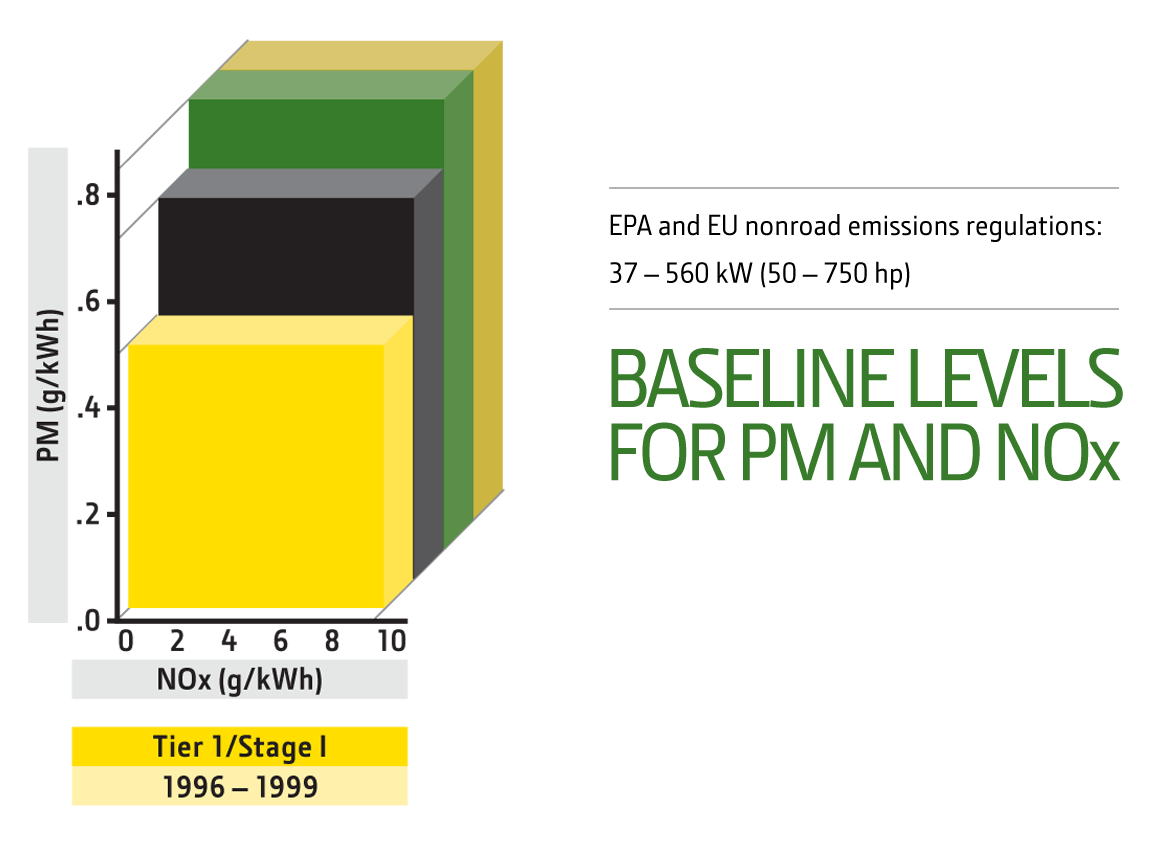
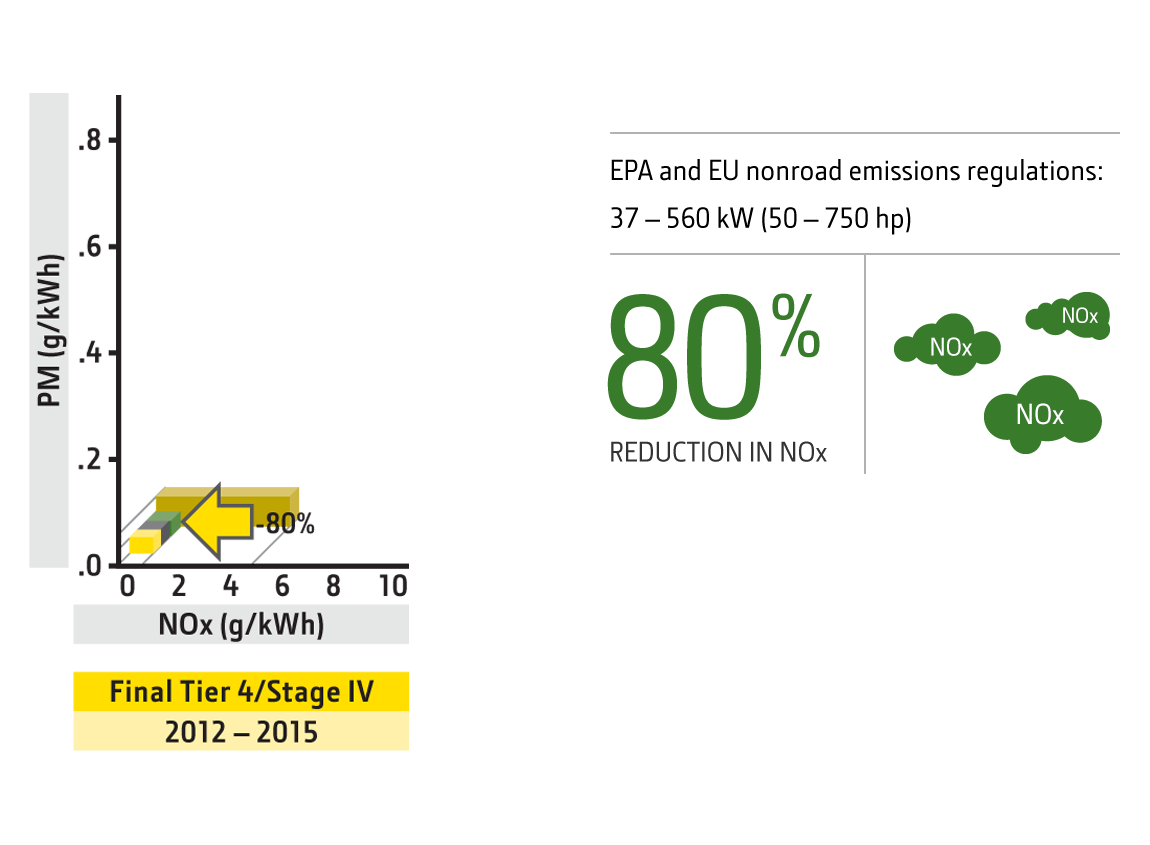
EPA and EU nonroad emissions regulations: 37 – 560 kW (50 – 750 hp)
Tier 1
1996 Tier 1/Stage I Technology
Emissions Target
Achieve established baseline levels for PM and NOx
Technology
- Engine Calibration
Optimized to lower emissions and improve performance. - Higher-Pressure Fuel System
High-pressure rotary pumps and more use of in-line pumps help reduce PM. - 2- or 4-Valve Cylinder Head
Models with 2-valve cylinder heads offer excellent engine breathing, while 4-valve cylinder heads provide increased airflow for emissions reduction. - Multiple Aspirations
Naturally aspirated, turbocharged, air-to-water, and air-to-air engine models available. The higher the aspiration, the more emissions reduction. - Larger Displacements
Increased displacements in all engine models help lower combustion temperatures and NOx. - Directed Top Liner Cooling
Directed top liner cooling contributes to improved oil control and reduced PM (8.1L, 10.5L, 12.5L).
Customer Benefit
- Improved Fuel Efficiency
Improved engine design delivers new levels of fuel efficiency and lower operating costs. - Increased Power Density
PowerTech engines have a higher power density that allows smaller, high-performing platform sizes and lowers installed costs. - Increased Power Range
Increased maximum power range to 373 kW (500 hp). - Power Bulge
Meets short-term power demands, increases torque response, and improves overall machine productivity. - Higher Peak Torque
Improves transient response for greater machine productivity. - Minimal Hardware & Mounting Location Changes
Common mounting points simplify the transition between emissions regulations. - Emissions Compliance
PowerTech engines meet emissions regulations without sacrificing engine performance.
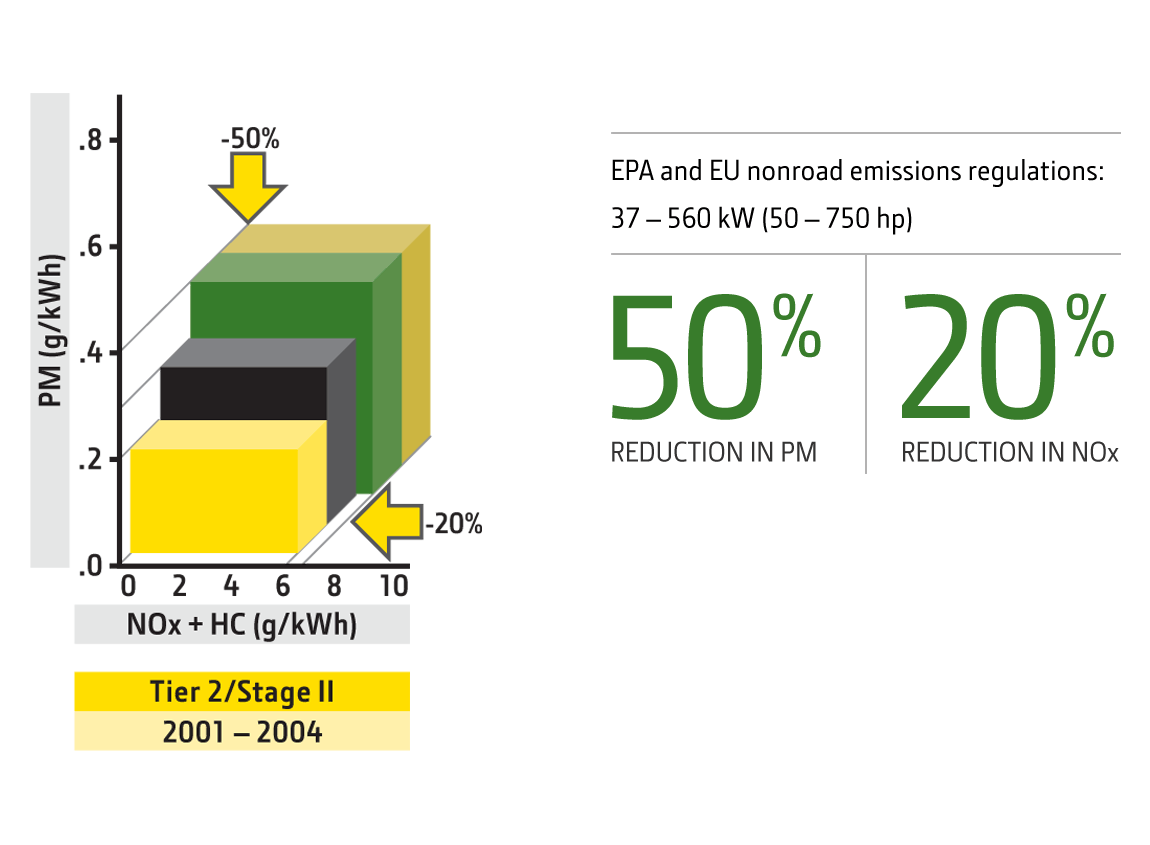
Tier 2
2001 PowerTech Tier 2/Stage II Technology
Emissions Target
50% reduction in PM
20% reduction in NOx
Technology
- Engine Calibration
Optimized to lower emissions and improve performance.
- Full Authority Electronic Engine Controls
Utilising more electronic controls improves engine calibration and lowers emissions.
- Higher-Pressure Fuel System
Electronically controlled rotary fuel pumps and high-pressure common-rail fuel system help reduce PM (8.1L, 4.5L, 6.8L).
- 2- or 4-Valve Cylinder Head
2-valve cylinder heads offer excellent engine breathing, while 4-valve cylinder head models provide increased airflow for emissions reduction.
- Air-to-Air Cooling Enhancements
More use of air-to-air aftercooling helps reduce emissions.
- Directed Top Liner Cooling
Directed top liner cooling contributes to improved oil control and reduced PM (8.1L, 12.5L).
Customer Benefit
- Improved Fuel Efficiency
Improved engine technologies deliver new levels of fuel efficiency and lower operating costs. - Increased Power Density
PowerTech Tier 2/Stage II engines have increased power density for each engine platform. Their compact size allows smaller, high-performing platforms and lower installed costs. - Increased Power Range
Increased maximum power range to 448 kW (600 hp). - More Power Bulge
Higher power bulge offered on more engine models. Meets short-term power demands, increases torque response, and improves overall machine productivity. - Higher Peak Torque
Improves transient response for greater machine productivity. - Improved Low-Speed Torque
Increased torque at lower engine speeds for better low-speed operation. - Minimal Hardware & Mounting Location Changes
Common mounting points simplify the transition between emissions regulations. - Emissions Compliance
PowerTech engines meet emissions regulations without sacrificing engine performance.
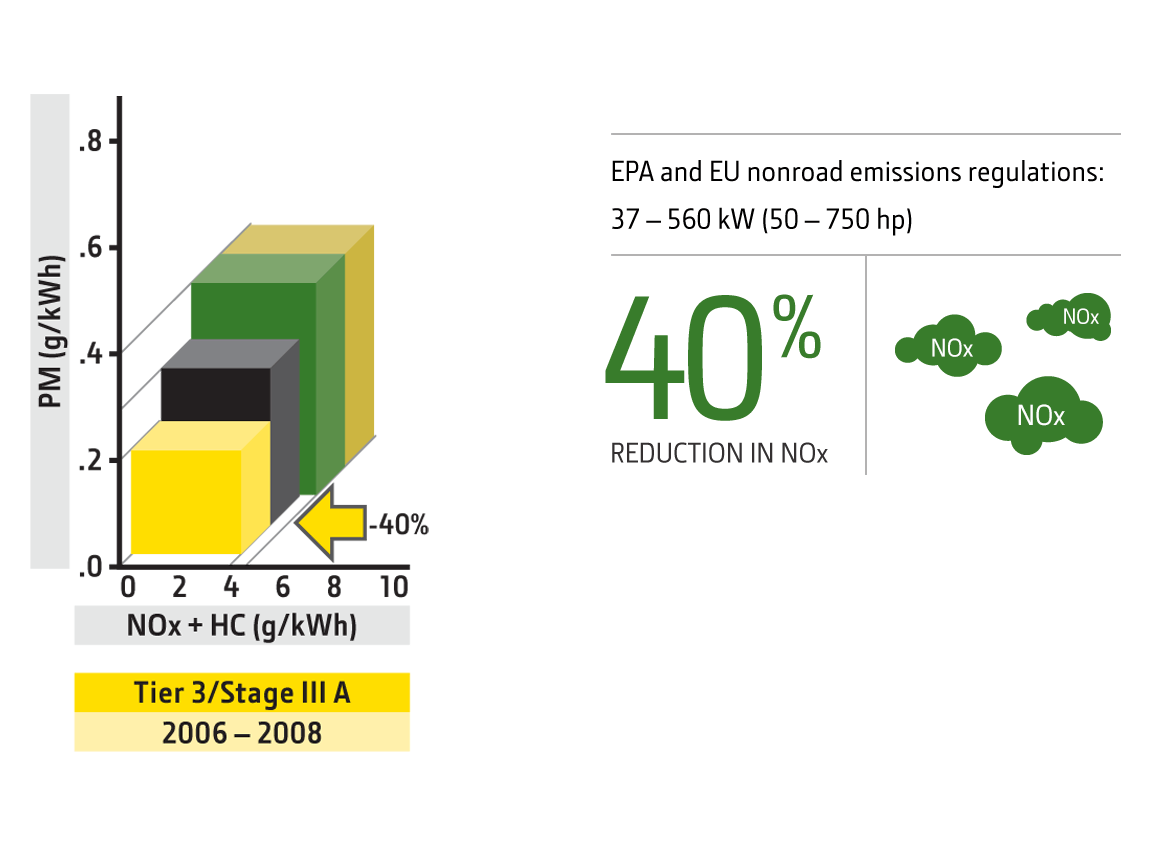
Tier 3
2006 PowerTech Tier 3/Stage III A Technology
Emissions Target
40% reduction in NOx
Technology
- Engine Calibration
Optimized to lower emissions and improve performance.
- Larger Displacements
Increased displacements in 9.0L and 13.5L models help lower combustion temperatures and NOx.
- Cooled EGR & VGT
Allows cooled exhaust gas to mix with incoming fresh air, lowering combustion temperature and reducing NOx.
- Full Authority Electronic Engine Controls
Utilising more electronic controls improves engine calibration and lowers emissions.
- Higher-Pressure Fuel System
Expanded use of electronic unit pumps (2.4L, 3.0L) and high-pressure common-rail fuel systems (4.5L, 6.8L) helps reduce PM.
- Air-to-Air Cooling Enhancements
More use of air-to-air aftercooling and lower charge air cooler outlet temperatures help reduce emissions.
- Directed Top Liner Cooling
Directed top liner cooling contributes to improved oil control and reduced PM (9.0L, 13.5L).
- 4-Valve Cylinder Head
Expanded use of 4-valve cylinder head technology (4.5L, 6.8L, 9.0L, 13.5L) provides increased airflow through the engine and reduces emissions.
- Low Sulfur Diesel
EPA and EU mandates for use of low sulfur diesel fuels lower PM.
Customer Benefit
- Best-in-Class Fuel Efficiency
PowerTech Plus Tier 3/Stage III A engines established an unparalleled record of best-in-class fuel economy. - Increased Power Density
PowerTech Tier 3/Stage III A engines have maintained or increased power density for each engine platform. You may be able to do the same job with a smaller displacement engine, which lowers total installed costs. - Power Bulge
Higher power bulge offered on all engine models. Meets short-term power demands, increases torque response, and improves overall machine productivity. - Higher Peak Torque
Improves transient response for greater machine productivity. - Improved Low-Speed Torque
Increased torque at lower engine speeds for better low-speed operation. - Multiple Rated Speeds
Multiple speeds provide application flexibility for reduced engine noise and improved fuel economy. - Emissions Compliance
PowerTech engines meet emissions regulations without sacrificing engine performance.
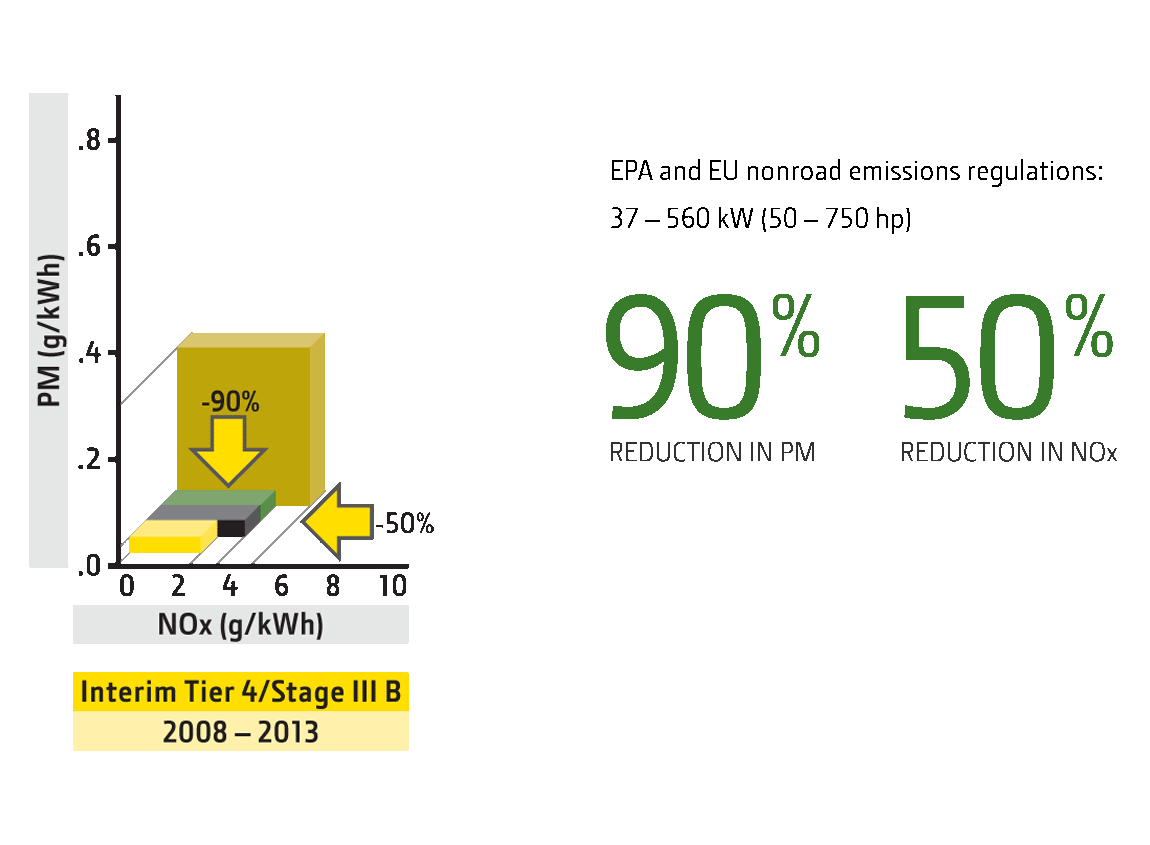
Interim Tier 4
2011 PowerTech Interim Tier 4/Stage III B Technology
Emissions Target
90% reduction in PM
50% reduction in NOx
Technology
- Engine Calibration
Optimized to lower emissions and improve performance.
- Higher-Pressure Fuel System
Expanded use of electronic unit pumps (2.4L), high-pressure common-rail (4.5L, 6.8L, 9.0L), and electronic unit injectors (13.5L) help reduce PM.
- Enhanced Cooled EGR with Venturi Flow Measurement
Allows higher and precise amounts of cooled exhaust gas to mix with incoming fresh air, lowering combustion temperature and reducing NOx.
- Series Turbochargers
Splitting the compression of air between two turbochargers allows for higher air intake pressures, improving airflow and reducing emissions.
- Smart Exhaust Filter
Smart exhaust filters utilise a DOC and DPF along with exhaust temperature management (ETM) to reduce PM downstream of the engine.
- Exhaust Temperature Management (ETM)
ETM adjusts injection timing, controls idle speed, and calibrates the engine to raise exhaust temperature and oxidize any PM that is trapped in the DPF.
- 4-Valve Cylinder Head
Expanded use of 4-valve cylinder head technology provides increased airflow through the engine for lower emissions.
- Directed Top Liner Cooling & Steel Piston
Directed top liner cooling and one-piece steel piston with oil-cooled gallery contribute to improved oil control and reduced PM (9.0L, 13.5L).
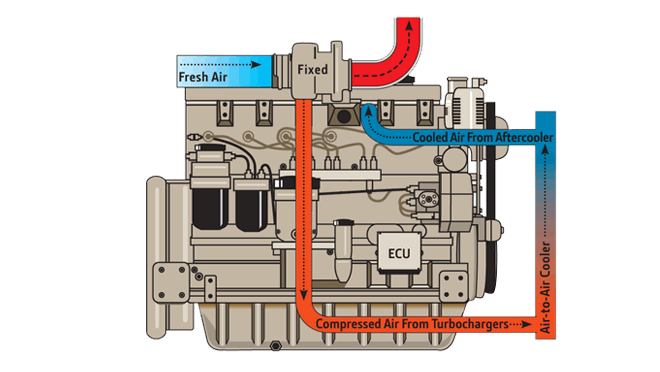
- Air-to-Air Cooling
Most models utilise air-to-air aftercooling and lower charge air cooler outlet temperatures to help reduce emissions.
- Variable-Speed Fan Drive
Optional factory-installed variable-speed fan drive improves fuel economy and reduces emissions.
- Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel
EPA and EU mandates for use of ultra-low sulfur diesel fuels lower PM.
Customer Benefit
- Single-Fluid Emissions Solution
PowerTech Interim Tier 4/Stage III B engines meet emissions regulations without using diesel exhaust fluid (DEF). - Right Technology for PM & NOx Reduction
John Deere provides an optimized solution using the right combination of emissions-reduction components to maximize performance while meeting regulations. - Improved Fuel Efficiency
PowerTech Interim Tier 4/Stage III B engines continue our unparalleled record of best-in-class fuel economy. - Minimal Operator Involvement
The single-fluid approach of cooled EGR means it is easy for operators to use and doesn’t require additional fluids. In most cases, exhaust filter regeneration does not impact machine operation or require operator involvement. - Increased Power Density
PowerTech Interim Tier 4/Stage III B 9.0L engines have increased power density. Their compact size allows a smaller, high-performing platform and lower installed cost. - Power Bulge
Higher power bulge offered on all engine models. Meets short-term power demands, increases torque response, and improves overall machine productivity. - Higher Peak Torque
Improves transient response for greater machine productivity. - Improved Low-Speed Torque
Increased torque at lower engine speeds for better low-speed operation. - Improved High-Altitude Performance (PSX models)
Series turbocharging delivers higher power density and improved high-altitude operation. - Improved Transient Response
Faster transient response times of PowerTech engines provide greater machine productivity. - Noise Reduction Improvements
The smart exhaust filter, multiple rated speeds, and variable-speed fan drive option provide noise reduction. - Emissions Compliance
PowerTech engines meet emissions regulations without sacrificing engine performance.
Final Tier 4
2014 PowerTech Final Tier 4/ Stage IV Technology
Emissions Target
80% reduction in NOx
Technology
- Engine Calibration
Optimized to lower emissions and improve performance.
- Higher-Pressure Fuel System
Electronic unit injector (13.5L) and high-pressure common-rail (4.5L, 6.8L, 9.0L) fuel systems increase fuel pressure to help reduce PM.
- Integrated Emissions Control System
The John Deere Integrated Emissions Control system is built on a proven platform of emissions control technologies including cooled exhaust gas recirculation (EGR), exhaust filters, and selective catalytic reduction (SCR) to achieve lower emissions.
- Enhanced Cooled EGR with Venturi Flow Measurement
Allows precise amounts of cooled exhaust gas to mix with incoming fresh air, lowering exhaust temperature and reducing NOx.
- Series Turbochargers
More use of series turbocharging (4.5L, 6.8L, 9.0L). Splitting the compression of air between two turbochargers allows for higher air intake pressures, improving airflow and reducing emissions.
- Smart Exhaust Filter
Smart exhaust filters utilise a DOC and DPF controlled by an exhaust temperature management (ETM) system to reduce PM.
- Exhaust Temperature Management (ETM)
ETM adjusts injection timing, controls idle speeds, and calibrates the engine to raise exhaust temperature and oxidize any PM that is trapped in the DPF or deposits that may form in the SCR components.
- Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)
SCR converts NOx to nitrogen and water vapour by mixing diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) with engine exhaust gases in the SCR catalyst — reducing NOx emissions downstream of the engine.
- 4-Valve Cylinder Head
Expanded use of 4-valve cylinder head technology provides increased airflow through the engine for lower emissions.
- Directed Top Liner Cooling & Steel Piston
Directed top liner cooling and one-piece steel piston with oil-cooled gallery contribute to improved oil control and reduced PM (6.8L, 9.0L, 13.5L).
- Air-to-Air Cooling
Most models utilise air-to-air aftercooling and lower charge air cooler outlet temperatures to help reduce emissions.
- Variable-Speed Fan Drive
Optional factory-installed variable-speed fan drive improves fuel economy and reduces emissions.
- Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel
EPA and EU mandates for use of ultra-low sulfur diesel fuels lower PM.
Customer Benefit
- Minimal Operator Involvement
Filter cleaning is automatic with minimal operator involvement. Low DEF usage requires fewer fill ups and minimizes DEF fluid handling. - Right Technology for PM & NOx Reduction
The John Deere Integrated Emissions Control system provides an optimized solution using the right combination of emissions-reduction components to maximize performance and fluid economy while meeting regulations. - World-Class Total Fluid Economy
Final Tier 4/Stage IV engines use less diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) than SCR-only systems, while delivering improved performance and world-class diesel fuel economy. - Longer Interval Between Active Filter Cleaning
Higher-pressure fuel systems extend the intervals between automatic cleanings, while helping achieve emissions compliance. - Extended Ash Service Interval
Ash service intervals of up to 15,000 hours can be achieved. In many cases, ash service may not be required until the first major engine overhaul. - Power Bulge
Higher power bulge offered on all engine models. Meets short-term power demands, increases torque response, and improves overall machine productivity. - Higher Peak Torque
Improves transient response for greater machine productivity. - Improved Low-Speed Torque
Increased torque at lower engine speeds for better low-speed operation. - Improved High-Altitude Performance
Series turbocharging delivers higher power density and improved high-altitude operation. - Improved Transient Response
Faster transient response times of PowerTech engines provide greater machine productivity. - Noise Reduction Improvements
The smart exhaust filter, multiple rated speeds, and variable-speed fan drive option provide noise reduction. - Emissions Compliance
PowerTech engines meet emissions regulations without sacrificing engine performance.
Videos
Final Tier 4/Stage IV Technology and Benefits